Welcome to our comprehensive Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) tutorial.
EDI is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way businesses communicate.
It allows the transfer of data from one computer system to another by standardized message formatting, without the need for human intervention.
In this tutorial, we will cover the essential aspects of EDI, from its fundamental principles and benefits to the actual steps of implementing EDI transactions in various business scenarios.
Whether you’re a complete novice or looking to refine your knowledge, this guide will help you understand how EDI can streamline your business processes and improve efficiency.

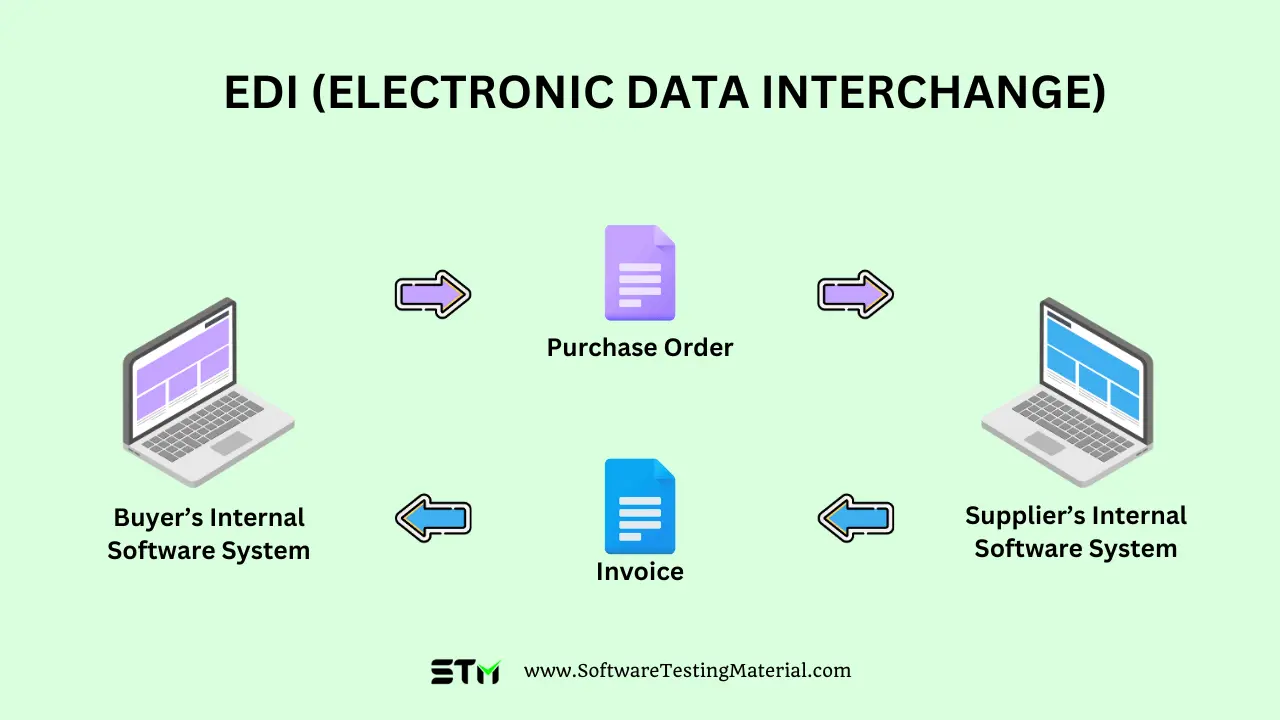
EDI, or Electronic Data Interchange, is a structured method by which businesses can electronically exchange documents and information.
It represents a standardized communication method between trade partners to transfer data such as purchase orders, invoices, inventory details, and shipping statuses.
Utilizing EDI, companies can improve efficiency and reduce errors by minimizing the need for manual data entry, ensuring that transactions are processed quickly and accurately.
This digital exchange of information is critical in today’s fast-paced business environment, allowing for time-sensitive data to be communicated instantaneously while also streamlining and automating the workflow between different systems and organizations.
The types of EDI can be categorized based on how the electronic documents are transmitted between trading partners. The three primary types of EDI are:
By employing these various types of EDI, businesses can choose the most efficient and cost-effective method for their specific needs, ensuring seamless and secure communication in their trade partnerships.
The benefits of EDI are as follows
#1. Saves Time & Money: EDI technology automates manual paper-based processes, saving time and costs. It ensures instant delivery of business documents, enabling faster decision-making.
#2. Reduces Errors: EDI ensures automated processing to reduce manual errors and detect anomalies for improved accuracy and efficiency in document processing. Strict standardization in EDI data transfer guarantees accurate formatting before integration into business processes or applications.
#3. Improves Efficiency & Productivity: EDI solutions enhance efficiency and productivity by facilitating the swift and accurate sharing and processing of a higher volume of business documents in less time.
#4. Improves Traceability & Reporting: EDI automation supports positive customer experiences by enabling efficient transaction execution and prompt, reliable product and service delivery.
#5. Positive Customer Experience: Integrating EDI enhances traceability and reporting by merging electronic documents with diverse IT systems to streamline data collection, visibility, and analysis.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) operates by allowing the transfer of standardized data between different business systems or entities. It typically follows this multi-step process:

This streamlined communication process minimizes manual entry, speeds up business transactions, and reduces errors, all while allowing systems to interact regardless of their native languages or technologies.
In conclusion, the adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) represents a substantial stride toward operational business excellence.
By automating the exchange of crucial business documents, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy, speed, and efficiency, leading to cost savings and improved business relationships.
As we’ve explored throughout this tutorial, EDI’s benefits are far-reaching, impacting various facets of an organization from supply chain management to customer satisfaction.
While the implementation of EDI may require careful planning and investment, the long-term advantages it provides are indisputable. We encourage businesses to embrace this transformative technology to maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving digital marketplace.